Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions. The term may also be applied to any machine that exhibits traits associated with a human mind such as learning and problem-solving.
The ideal characteristic of artificial intelligence is its ability to rationalize and take actions that have the best chance of achieving a specific goal. A subset of artificial intelligence is machine learning, which refers to the concept that computer programs can automatically learn from and adapt to new data without being assisted by humans. Deep learning techniques enable this automatic learning through the absorption of huge amounts of unstructured data such as text, images, or video.
- Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines.
- The goals of artificial intelligence include learning, reasoning, and perception.
- AI is being used across different industries including finance and healthcare.
- Weak AI tends to be simple and single-task oriented, while strong AI carries on tasks that are more complex and human-like.
The traditional problems (or goals) of AI research include reasoning, knowledge representation, planning, learning, natural language processing, perception and the ability to move and manipulate objects. AGI is among the field’s long-term goals. Approaches include statistical methods, computational intelligence, and traditional symbolic AI. Many tools are used in AI, including versions of search and mathematical optimization, artificial neural networks, and methods based on statistics, probability and economics. The AI field draws upon computer science, information engineering, mathematics, psychology, linguistics, philosophy, and many other fields.
Checkout this video to know all about artificial intelligence(AI):
General perception of people about RÔBÓT
In the next few years, robots will be part of our everyday lives (Fujita and Kitano, 1998; Goldberg, 2001; Lee et al., 2010; Kee, 2011). Technological progress in robotics is accelerating exponentially and the introduction of social robots in some regions of the world is already a reality. Much effort has also been devoted to increasing the acceptance of social robots by giving them more and more human features, such as a national identity and citizenship.However, it remains unclear how attributing human social constructs such as nationality to robots impacts the way they are perceived by people in general. One’s country of origin is certainly far from being an anodyne piece of information in the eyes of many individuals.
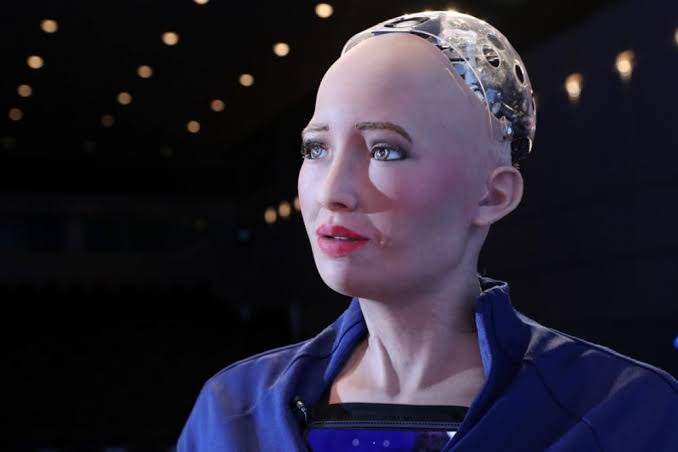

Sophia is a social humanoid robot developed by Hong Kong-based company Hanson Robotics. Sophia was activated on February 14, 2016, and made her first public appearance at South by Southwest Festival (SXSW) in mid-March 2016 in Austin, Texas, United States.
Sophia has been covered by media around the globe and has participated in many high-profile interviews. In October 2017, Sophia “became” a Saudi Arabian citizen, the first robot to receive citizenship of any country. In November 2017, Sophia was named the United Nations Development Programme’s first ever Innovation Champion, and is the first non-human to be given any United Nation title.

Checkout this video to watch sophia’s interview:
Checkout this video to know what sophia said about humans:
In January 2018, Facebook’s director of artificial intelligence, Yann LeCun, tweeted that Sophia was “complete bullshit” and slammed the media for giving coverage to “Potemkin AI”. In response, Goertzel stated that he had never pretended Sophia was close to human-level intelligence.
Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL), the latter has been one of the most used keywords in some conferences in robotics recently, are consolidated topics embraced by the robotics community nowadays.A number of other robotics-related products are starting to be commercially available for increasingly complex tasks such as visual question and answering systems, video captioning and activity recognition, large-scale human detection and tracking in videos, or anomaly detection in images for factory automation.
Once a robot is (self) localized, it can proceed with the execution of its task. In the case of autonomous mobile manipulators, this involves localizing the objects of interest in the operating environment and grasping them. In a typical setup, the robot navigates to the region of interest, observes the current scene to build a 3D map for collision-free grasp planning and for localizing target objects. There are cases where a tighter integration of perception and manipulation is required, e.g., for high-precision manipulation, where approaches like visual servoing are employed. However, in every application, there is a potential improvement for treating perception and manipulation together.
Scope of ÃĪ

Artificial Intelligence is one of the fastest-growing sectors in the tech sector. And as you can see clearly, the scope of AI has expanded into many sectors, including healthcare, transport, and security. Due to such growth, multiple industries require the expertise of skilled AI professionals.
The technology that makes all these things possible is termed Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (MI). Artificial Intelligence can be seen as the intelligence of machines through which they try to mimic human intelligence. With the increasing scope of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in India, machines could be trained in certain circumstances to decide on their own. The scope of Artificial Intelligence in India is still in the adoption stage but slowly it is being used to find smart solutions to modern problems in almost all the major sectors such as Agriculture, Healthcare, Education and Infrastructure, Transport, Cyber Security, Banking, Manufacturing, business, Hospitality, Entertainment. Aspirants who are looking to pursue an Artificial Intelligence course can read this article. By going through this article candidates will get an idea about the scope of Artificial Intelligence in India.
The scope of Artificial Intelligence in India is promising. Artificial Intelligence has immense potential to change each sector of the economy for the benefit of society. There is not just one technology under AI, but there are various useful technologies such as self-improving algorithms, machine learning, big data, pattern recognition.
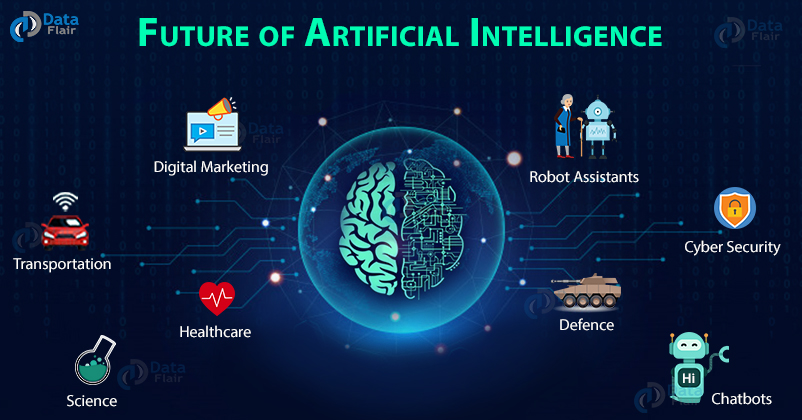
AI in Cyber Security
Cybersecurity is another field that’s benefitting from AI. As organizations are transferring their data to IT networks and cloud, the threat of hackers is becoming more significant.
AI in Healthcare
The medical sector is also using this technology for its advantages. AI is helping medical researchers and professionals in numerous ways.
The Knight Career Institute and Intel have made a collaborative cancer cloud. This cloud takes data from the medical history of cancer (and similar) patients to help doctors in making a better diagnosis. Preventing cancer from moving to higher stages is its most effective treatment at this time.
AI in Transport
The transport sector has been using AI for decades. Airplanes have been using autopilot to steer them in the air since 1912. An autopilot system controls the trajectory of a plane, but it isn’t restricted to aircraft alone. Ships and spacecraft also use autopilot to help them maintain the correct course.
AI in Science and Research
AI is making lots of progress in the scientific sector. Artificial Intelligence can handle large quantities of data and processes it quicker than human minds. This makes it perfect for research where the sources contain high data volumes.
AI is already making breakthroughs in this field. A great example is ‘Eve,’ which is an AI-based robot. It discovered an ingredient of toothpaste that can cure a dangerous disease like Malaria.
AI in chatbots
In a country as varied as India, the combination of chatbots in the digital framework or availability via the IVRS system education domain can be transformational– they might be educated on the subject matter and a great percentage of doubts of the pupils could be responded to quickly, consequently lowering the current work of educators who could focus on even more imaginative tasks.
AI in defence
The strength of its army is one of the factors indicating how powerful the country is. In some of the most developed nations, investment in this sector is the highest as compared to other sectors. AI-equipped military systems are capable of handling volumes of data efficiently. In addition to that, such systems have improved self-control, self-regulation, and self-actuation due to its superior computing and decision-making capabilities.
Not only are robots cool, they are also gradually taking over the industrial world. This field needs engineers or programmers that can program these robots to solve problems like a human would.
The Difference Between Emotional Intelligence and Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the theory and development of computer systems and computerized processes, to be able to perform tasks normally requiring human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision making and translation between languages. AI algorithms don’t need to be altered by a human hand, they do it automatically by analyzing information and finding current errors to prevent future problems. the key difference between emotional intelligence and artificial intelligence lies here.
Emotional intelligence is a skill that comparatively, focuses on manual labor, and can be mastered. It requires training and practice, but is necessary to live fuller and healthier lives. Emotional intelligence attempts to enhance an individual’s key personal emotional competencies as well emotional intelligence relationship skills for both personal and professional success.
The well-known author and spiritual authority Amit Ray recently said in an interview, that as more and more artificial intelligence comes into play in the modern workplace, we must infuse our business leadership skills with the various elements of emotional intelligence. There are numerous numbers of things that machines can do better than human beings, and we actually shouldn’t be very proud to admit it. With the inclusion of artificial intelligence in business, AI now has the capability to not only gather, analyze, and interpret data, but also to develop an action plan to carry out a solution.
At first, it seems rather alarming. Is there even something that machines do that humans can? The answer is simple: understanding, motivating, and actually talking with humans. This is where the role of emotional intelligence (EQ) comes in. Leaders who have the ability to empathize, energize, and develop meaningful, respectful relationships with their employees, in other words, leaders who possess emotional intelligence, will begin to achieve success in a constantly evolving and uncertain world.
What humans can offer to the business world that machines cannot, is the ability to relate and actually interact to the people around us, the primary difference between emotional intelligence and artificial intelligence. Machines will always have to learn how to develop their capacity to understand and interact with others, as well as develop their ability for compassion and empathy in order to be on the same level as humans.
Perhaps somewhere in the future, we humans will be able to develop an artificial intelligence that can relate to humans emotionally. Until then, we will have to nurture and train ourselves to highly value emotional intelligence and its various capacities, which previously was underestimated as a trait in the workforce.